- Home
- Shoulder Pain Causes
- SLAP Tear
SLAP Tear
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board
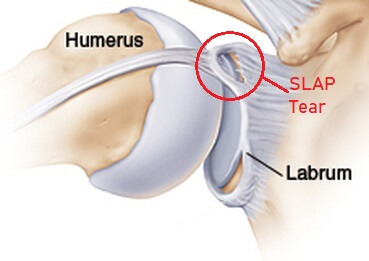
A SLAP tear is when there is damage to the ring of cartilage on the socket of the shoulder joint, known as the labrum.
SLAP stands for “superior labral anterior to posterior tear”, meaning a tear of the upper rim of the labrum, from front to back.
The glenoid labrum is most commonly injured by a fall or from repetitive overhead movements, such as racket sports or throwing activities.
Symptoms of a SLAP lesion usually include pain, weakness, instability and a catching sensation in the shoulder. SLAP tear treatment usually involves medication and physical therapy, but in some cases, surgery will be advised.
Here, we will look at the common causes, symptoms and treatment options for a SLAP tear.
What Is A SLAP Tear?
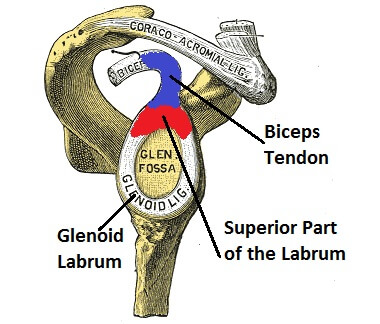
A SLAP tear occurs in the glenohumeral joint aka shoulder. This is where the top part of the arm bone (the head of humerus), which is shaped like a ball, fits in a socket on the front of the shoulder blade (glenoid fossa).
The shoulder socket is very shallow, similar to a golf tee, to allow for lots of movement.
To improve the stability of the shoulder, there is a ring of cartilage, known as the glenoid labrum, which helps to deepen the socket without restricting movement. The glenoid labrum is reinforced by the tendons of various muscles of the shoulder.
Shoulder labrum tears may develop may develop anywhere in the labrum, but SLAP tears are the most common.
With a SLAP tear, the top part of the glenoid labrum, which is reinforced by one of the biceps tendons, is torn. This top part of the labrum tears from away from the glenoid socket from front to back (anterior to posterior), often damaging the biceps tendon as well resulting in biceps tendonitis. Excess fluid may also pool near the SLAP tear, forming a paralabral cyst.
Types of Slap Tear
There are a number of different types of lesion, depending on the nature and severity of the injury. The four most common types of SLAP tear are:
- Type 1 SLAP Tear: Degeneration (wear and tear) where the edges of the labrum fray, but stay attached to the glenoid rim. Biceps tendon is unaffected
- Type 2 SLAP Tear: The superior (top) part of the labrum and the biceps tendon are torn off the glenoid rim
- Type 3 SLAP Tear: A bucket-handle tear of the labrum where part of the rim detaches forming a flap which can get caught in the joint, causing locking or catching sensations. The biceps tendon is unaffected
- Type 4 SLAP Tear: A bucket handle tear of the superior glenoid labrum which extends into the biceps tendon
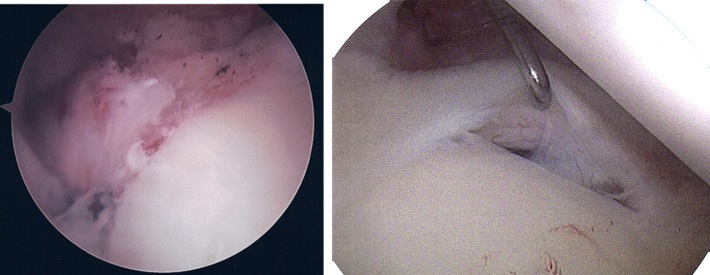
Type 1 and type 2 SLAP tears are the most common. Other parts of the shoulder are often damaged at the same time as a SLAP tears, such as:
- Bankart Lesions: damage to the bottom part of the glenoid labrum
- Rotator Cuff Tears: damage to one of the four main shoulder stabilisers
- Dislocated Shoulder: upper arm bone pops out of the shoulder socket
Common Causes of SLAP Tear
SLAP tears can develop suddenly through a one-off event, known as an acute injury, or gradually from repetitive movements, known as a chronic injury.
Acute Injuries
Acute SLAP tear injuries tend to affect younger people, under the age of 40 and are typically caused by:
- A Fall: most commonly onto an outstretch hand
- RTA: (road traffic accident) especially if you have pushed through your outstretched arms to brace yourself from the impact
- Shoulder Dislocation: when the head of humerus pops out of the glenoid socket
- Lifting: picking up a heavy object
- Sports Injury: such as a tackle, especially when your arm is above your head, or pulling down through the arm
Chronic Injuries
Chronic SLAP tears are usually caused by:
- Repetitive Movements: especially with the arm above the head such as throwing actions, racket sports or swimming
- Repetitive Heavy Lifting: which pulls down on the arm e.g. weight lifting
Chronic tears tend to occur in people over the age of 40, and degeneration of the glenoid labrum is often seen as part of the normal aging process, making it more prone to damage.
SLAP Tear Symptoms
The most common SLAP tear symptoms are:
- Pain: with shoulder movements or when lifting things above the head. It tends to be a dull ache, rather than a sharp pain
- Weakness: decreased strength in the upper arm
- Instability: it may feel as if the shoulder is going to “pop-out”. Often affects sleep as it can be difficult to get into a comfortable position as the shoulder drops slightly when lying on it due to the instability
- Difficulty Throwing: athletes may complain of a loss of strength and velocity (speed) when throwing
- Decreased Movement: range of motion at the shoulder may be reduced
- Catching Sensation: or a feeling of impingement (blocked movement) or shoulder clicking when moving the arm
Your doctor should be able to diagnose a SLAP tear from talking to you and examining your shoulder. They may also want to get x-rays or an MRI, often with contrast dye to get a clearer picture.
SLAP Lesion Treatment
SLAP tear treatment will depend on the type of lesion and the associated symptoms. Generally, conservative (i.e. non-surgical) treatment is tried first and if this fails, surgery will be considered.
#CommissionsEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Non-Surgical Treatment
Conservative, i.e. non surgical, treatment for a SLAP lesion will likely include:
- Medication: pain-relief and anti-inflammatories such as naproxen and ibuprofen/Advil can help to reduce pain and inflammation
- Rest: from aggravating activities to allow time for the tear to heal
- Physical Therapy: including exercises to regain the strength and movement of the shoulder - visit the rotator cuff exercises section to find out more
- Scapular Stabilisation: exercises to improve the strength and stability of the shouder are a vital part of rehab with a SLAP tear to prevent ongoing problems of pain and instability - find out more in the scapular stabilization exercises section
SLAP Tear Surgery
If you are still having problems after three to six months of rehab,
SLAP repair surgery may be advised. SLAP tear surgery is usually done
arthroscopically i.e. keyhole surgery. A small camera known as an arthroscope is
inserted into the shoulder joint so the surgeon can see exactly what
damage has been done.
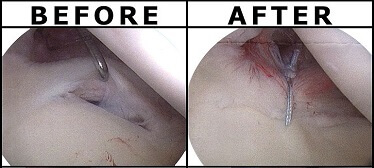
Surgical technique will depend on the type of tear. During SLAP tear surgery, the surgeon will debride (clean up) any frayed edges, remove any cysts and then either remove or reattach any torn parts of the glenoid labrum.
When reattaching torn segments, anchors are inserted into the bone of the shoulder socket and the torn glenoid labrum is sewn back together and held in the correct place with sutures attached to the anchors.
Recovering From Surgery
Following SLAP tear surgery, you will need to wear a sling initially for a few weeks (including in bed) to allow the shoulder to heal.
You will work with a physical therapist on a progressive rehab programme to regain the movement, strength and stability of your shoulder - you can find examples of helpful exercises in the rotator cuff exercises and scapular stabilization exercises sections. It usually takes 4-6 months to return fully to sports after surgery.
SLAP tear surgery is successful at reducing pain and instability and restoring function in most cases and complications are rare.
What Else Can Help?
It's not just the top of the labrum that is prone to damage, shoulder labrum tears can occur anywhere. Tears in the bottom part of the labrum are known as Bankart Lesions. A Bankart lesion commonly occurs with shoulder dislocations and there tends to be more shoulder instability associated with it than with SLAP tears.
The most common symptoms of labrum tears are a dull aching pain when lifting your arm above your head, shoulder instability, weakness and difficulty throwing. If you don't have these symptoms, chances are it's not a SLAP Tear but something else such as:
If you want help working out what is wrong, check out our shoulder pain diagnosis section.
Related Articles
Medical References
- NCBI: Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior Lesions by M. Varacallo, D. Tapscott, S. Mair
- International Journal Of Sports Phyiotherapy: The Recognition and Treatment of Superior Labral (SLAP) Lesions in the Overhead Athlete
- Radiopedia: Superior Labral Anterior Posterior Tear
Page Last Updated: May 21st, 2024
Next Review Due: May 21st, 2026