- Home
- Wrist Pain Diagnosis
- Inner Wrist Pain
Ulnar Wrist Pain
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board
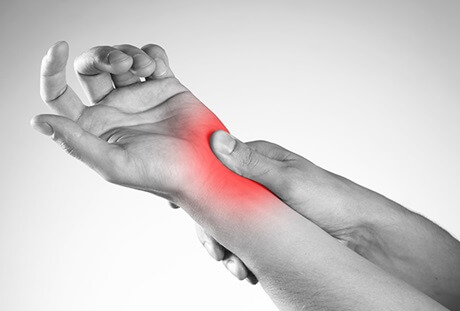
Ulnar wrist pain is a common problem where there is pain on the inner side of the wrist (pinky finger side).
The most common causes of pain on the inside of the wrist are a fall onto an outstretched hand and repetitive overuse.
It can often be managed with simple home treatments such as rest, wrist splints and exercises, but if there is significant instability or a fracture, then surgery may be required.
Here we will look at the common causes of ulnar wrist pain, typical symptoms, when to see a doctor, treatment options and prevention strategies. If your pain is in a slightly different place, check out the radial wrist pain and central wrist pain articles or have a look at our wrist pain charts.
What Causes Ulnar Wrist Pain?
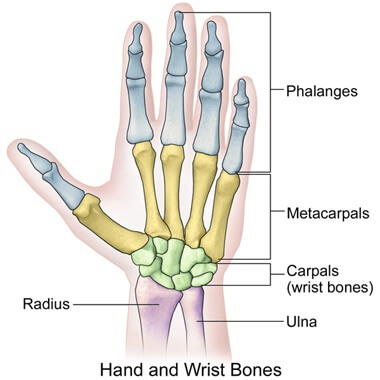
Inside wrist pain is usually caused by:
- Sudden Impact: typically a fall onto an outstretched hand, or a direct blow to the inside of the wrist
- Repetitive Stress: activities involving repetitive wrist and hand movements, e.g. typing, racket sports and heavy lifting
- Medical Conditions: some medical conditions increase the risk of developing pain on inside of wrist
The wrist is the joint between the forearm bones (radius and ulna) and the small hand bones (carpal bones) and is surrounded by various ligaments, tendons, muscles, cartilage and nerves.
Common causes of ulnar wrist pain include:
1. Bone Problems
Injuries to the ulna or the inner carpal bones is a common cause of inside wrist pain
- Wrist Fractures: a break in one of the wrist or hand bones, typically caused by falling onto an outstretched hand or forceful twisting. There is usually immediate pain and there may be an obvious deformity. The most common fractures causing ulnar wrist pain are ulnar styloid fractures, ulnar fractures, triquetral fractures, pisiform fractures and hamate fractures. FIND OUT MORE >
- Ulnar Impaction Syndrome: occurs when the ulnar is longer than it should be compared to the radius, causing it to repetitively butt-up against the carpal (hand) bones. The abnormal length may be genetic or may develop due to radius shortening after a fracture. Inner wrist pain from ulnar impaction syndrome develops gradually over a time.
2. Tendon Problems
Another common cause of pain on the inside of the wrist is irritation and inflammation of the medial wrist tendons, the most common being
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Tendonitis: causes ulnar wrist pain on the back of the wrist due to repetitive use. Typically affects athletes, office staff and construction workers. The inner wrist pain gets worse with gripping and twisting movements and is often associated with reduce grip strength and a clicking/snapping sensation. FIND OUT MORE >
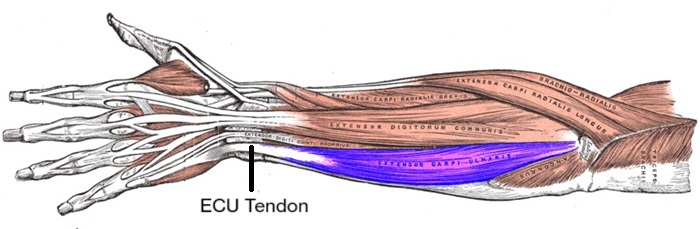
- Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Tendonitis: causes inside wrist pain on the front (palm side) of the wrist. Activities requiring repetitive wrist and hand flexion and ulnar deviation e.g. cutting hair, swimming and rock climbing are common causes. Activities such as holding a cup of coffee will often aggravate pain. FIND OUT MORE >
3. Ligament Problems
Damage to any of the inner wrist ligaments can cause ulnar wrist pain, the most common being:
- TFCC Injury: The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a complex structure made up of various ligaments that stabilises the inner wrist. It is usually injured by forced wrist extension or ulnar deviation (hand bends sideways towards pinky finger), or awkward twisting. Common symptoms include pain on inside of wrist, clicking, reduced grip strength and difficulty rotating the wrist. FIND OUT MORE >
- Wrist Sprain: over-stretching or tearing of one of the wrist ligaments. Wrist sprains are usually caused by a fall, sporting injury or RTA. Common symptoms include inside of wrist pain, swelling, bruising and reduced range of motion
4. Nerve Problems
The ulnar nerve travels from the neck down the inner side of the arm and wrist to the hand. Damage anywhere along the nerve can cause problems but the most common issue is:
- Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome: the ulnar nerve gets compressed as it travels through the inner wrist, usually due to a cyst, repetitive pressure or narrowing of the inner wrist tunnel (Guyon’s Canal). Common symptoms include ulnar wrist pain, tingling and numbness in the ring and little finger. This can affect grip strength and fine motor control.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is the most common nerve problem at the wrist but it tends to cause tingling and numbness more in the central part of the wrist and palm.
5. Medical Conditions
There are a number of medical conditions that can contribute to ulnar wrist pain:
- Arthritis: wear and tear of the cartilage and bone in the wrist joint, caused by aging, injury or chronic inflammation
- Ganglion Cyst: a sac of thick fluid that develops along the front or back of the wrist, forming a firm lump. Ganglions are usually completely harmless but may cause pain if they start to press on the surrounding structures. A wrist ganglion often fluctuates in size and may come and go. FIND OUT MORE >
- Ulnar Bursitis: inflammation of the ulnar bursa, the synovial tendon sheath that reduces friction between the flexor tendons on the inner wrist as they pass through the carpal tunnel. Ulnar bursitis is typically caused by repetitive friction on the bursa, causing inside wrist pain and swelling or a small lump on the front of the wrist
- Kienbock’s Disease: a rare condition where the blood supply to one of the small wrist bones, the lunate, is reduced. As a result the bone slowly deteriorates and dies. It causes dull inner wrist pain, tenderness over the lunate bone, weakness, swelling and stiffness.
Common Symptoms With Ulnar Wrist Pain
The symptoms of ulnar wrist pain often include:
- Pain: on inside of wrist that typically gets worse with movement and gripping
- Clicking: with movement especially twisting
- Reduced Grip Strength: and weakness in the wrist and hand
- Reduced Motion: stiffness and loss of wrist movement
- Tingling: and numbness if there is nerve damage
When To See A Doctor
You should see your regular doctor for ulnar wrist pain if you have:
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks
- Swelling, stiffness, or reduced grip strength
- Clicking, popping, or grinding in the wrist
- Pain worsening with activity or certain movements
- History of repetitive wrist use or prior injury
A hand/wrist specialist (orthopedic doctor or physical therapist) may be needed if symptoms don’t improve with rest and basic treatment.
You should seek urgent medical attention if you have:
- Severe pain after trauma e.g. fall, direct impact
- Visible deformity in the wrist
- Inability to move the wrist or fingers
- Persistent numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hand
- Severe swelling or bruising
If you are unsure, if is best to consult a doctor early to get an accurate diagnosis and ensure effective treatment.
#CommissionsEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Ulnar Wrist Pain Treatment
Ulnar wrist pain treatment will depending on the underlying cause of your inner wrist pain but may involve a combination of:
- Rest: from aggravating activities and try to avoid anything with increases your pain to give your wrist time to heal
- Ice: regularly applying an ice pack to the wrist can help reduce inner wrist pain and inflammation and in turn speed up healing
- Compression: wearing a tubigrip compression bandage helps to support the wrist and reduce any swelling
- Elevation: if there is any swelling in the wrist, keep the hand elevated higher than the level of your heart when possible e.g. by wearing a sling
- Wrist Support/Splint: elasticated wrist supports are a great way to provide some support and stability to the wrist but still allow some movement, making them perfect for conditions such as tendonitis. Wrist splints have a metal bar in them which prevents wrist flexion which is more suitable for wrist fractures and carpal tunnel syndrome
- Medication: over-the-counter painkillers e.g. paracetamol/acetaminophen and anti-inflammatories e.g. ibuprofen can help reduce ulnar wrist pain and swelling
- Corticosteroid Injections: can help to reduce inside wrist pain and inflammation
- Desk Setup: changing your desk set up can help reduce stress and pressure on the wrist. Two of the best options are cushioned keyboard pads and an ergonomic mouse
- Exercises: a physical therapist can recommend a program of strengthening, stretching and stability exercises to improve wrist strength, flexibility and control
- Functional Aids: if your grip strength is affected, there are various aids you can get to help with everyday tasks e.g. jar openers
- Ergonomic Changes: it may help to change your hand position during work/sport/activities e.g. how you hold rackets or tools
- Surgery: some instances of inside wrist pain may require surgery e.g. wrist fractures, nerve compression or ligament ruptures. This may be done arthroscopically (keyhole) or with open surgery
Preventing Wrist Injuries
Whilst it is not always possible to avoid wrist injuries, there are some simple things you can do to reduce your risk of developing ulnar wrist pain:
- Avoid Overuse: take regular breaks from repetitive tasks
- Wear Protective Gear: such as wrist guards or braces with high risk activities e.g. skateboarding
- Strengthen & Stretch: do wrist and forearm strengthening and stretching exercises to improve flexibility, strength and stability
- Desk Set Up: Use keyboard pads and an ergonomic mouse to reduce the pressure and strain on the wrist
- Reduce Fall Risk: remove rugs or any trip hazards from home and use a cane or walker when out if you have any balance issues. Be careful on wet or uneven surfaces e.g. cobblestones, curbs, steps and stairs
- Don’t Overreach: Use a stable ladder when reaching for things rather than standing on a stool or chair
Ulnar Wrist Pain Summary
Ulnar wrist pain is a common problem where there is pain or discomfort on the inner (pinky) side of the wrist.
The most common causes of inner wrist pain are ulnar fractures, tendonitis and wrist sprains, typically from falls or overuse.
Ulnar wrist pain treatment usually involves a combination of RICE, wrist splints, exercises and ergonomic adjustments, but in some cases, surgery may be necessary.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Outer Wrist Pain
- Central Wrist Pain
- Distal Radius Fractures
- Wrist Fractures
- Lump On Wrist
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Wrist Pain Diagnosis Chart
- Forearm Pain Diagnosis
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis
Related Articles
Shoulder Problems
November 6th, 2024
Diagnosis Charts
June 12th, 2024
Rehab Exercises
December 12, 2023
Medical & Scientific References
- Anatomy, Shoulder And Upper Limb, Hand Ulnar Bursa. National Library Of Medicine
- Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain. Part I: Anatomy And Physical Examination. Skeletal Radiology
- Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain. Current Reviews In Musculoskeletal Medicine
- Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain in the Athlete: Sport-Specific Demands, Clinical Presentation, and Management Options. Current Sports Medicine Reports
Page Last Updated: March 17th, 2025
Next Review Due: MArch 17th, 2027