- Home
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis
- Elbow Bursitis
Olecranon Bursitis
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board

Olecranon bursitis is a common cause of pain and swelling at the back of the elbow.
Also known as Student's Elbow or Elbow Bursitis, it develops when there is irritation and swelling in the olecranon bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac.
Olecranon bursitis may or may not be painful, depending on the amount of swelling and whether there is an associated infection.
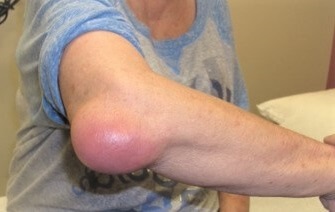
If you think your elbow is looking a bit like Popeye’s elbow with a lump, bulge or pocket of swelling at the back, chances are you have elbow bursitis.
Here we will look at the common causes and symptoms of olecranon bursitis, how it is diagnosed and treated and when you should see your doctor.
What Is Olecranon Bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis is a common cause of elbow swelling where there is inflammation of the olecranon bursa at the back of the elbow.
The olecranon process is the bony tip of your elbow, located on the end of the ulna - one of the forearm bones. The olecranon is the pointy bit that sticks out at the back of your elbow when you bend your arm or rest your elbow on the table.
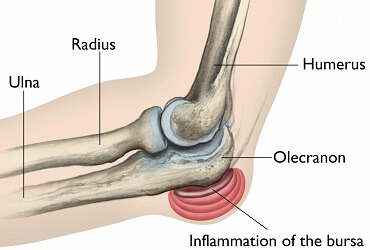
The olecranon bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that sits between the olecranon process and the overlying skin.
Its job is to protect and cushion the elbow and to allow the skin, tendons and ligaments to move freely over the ulna bone.
Normally, the olecranon bursa rests flat against the elbow so you don’t even notice it, but if it becomes irritated, it starts to swell and you soon know about it.
There are lots of different names for olecranon bursitis: elbow bursitis, popeye elbow, baker’s elbow, student’s elbow, miner’s elbow, plumber’s elbow, draftsman’s elbow and swellbow, but they all refer to the same thing. Bursitis is the most common cause of swelling and pain behind the elbow.
What Causes Olecranon Bursitis?
Common causes of olecranon bursitis include:
- Injury: a sudden, hard blow to the back of the elbow e.g. falling onto your elbow or bashing it against something. Swellbow often affects skateboarders
- Repetitive Pressure: on the olecranon bursa from leaning through your elbow on a hard surface for prolonged periods. This commonly affects students and office workers who lean on their elbows as they work, or trades people such as plumbers, who end up crawling and leaning through their elbows a lot
- Repetitive Friction: on the bursa from repetitive elbow movements. Most commonly in athletes who do lots of throwing e.g. baseball, cricket and javelin throwers, or weightlifters
- Medical Conditions: certain medical conditions that cause inflammation can increase your risk of developing olecranon bursitis e.g. arthritis, gout and kidney failure
- Infection: A cut, scrape or insect bite in the skin over the olecranon process can let micro-organisms (typically bacteria) into the bursa. Septic infections cause excess fluid to collect in the olecranon bursa and the elbow will appear red, swollen and hot. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of septic olecranon bursitis
Any of these things can cause inflammation of the lining of the olecranon bursa. The bursa reacts by producing extra fluid in an attempt to protect and heal itself. This excess fluid accumulates and is contained in the sac – think of the bursa as being like a water balloon, so the bursa begins to swell resulting in olecranon bursitis.
Elbow Bursitis Symptoms
Common symptoms of olecranon bursitis include:
- Swelling: at the back of the elbow. The swelling is usually confined to the bursa so there will be an obvious lump similar to a golf ball or small orange. The swelling may build up gradually or rapidly depending on the underlying cause and tends to be soft rather than hard. Olecranon bursitis is the most common cause of a lump on elbow
- Elbow Pain: Student's elbow may or may not be painful but tends not to be severe. Often the pain is worse when you bend your elbow or put any pressure through the bursa such as leaning on a desk. If the bursa gets infected it often becomes more painful
- Redness & Heat: Septic elbow bursitis, where there is an infection in the bursa, will usually cause redness in the skin over the bursa and it may feel warm to touch. Infected olecranon bursitis may also be accompanied by a fever. In severe cases, the infection may spread through the body and can cause serious illness. Around one third of cases of olecranon bursitis are septic
Olecranon bursitis doesn’t usually limit elbow movement.
Diagnosing Student's Elbow
Doctors can diagnose most cases of olecranon bursitis simply by examining your elbow, without the need for further tests.
In some cases, they may send you for an x-ray or ultrasound scan to check for an underlying fracture or bone spur.
If they suspect there may been an infection, aka septic olecranon bursitis, or gout, then your doctor will drain some of the fluid, known as aspiration, and send it for analysis. Normal bursa fluid is clear or straw coloured, but if you have an infection, it can turn to pus and the fluid may be cloudy, milky, yellowy, green or even brown.
#CommissionsEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Elbow Bursitis Treatment
Most cases of olecranon bursitis can be treated with a combination of:
- Ice: Regularly applying an ice pack to the back of the elbow for 10 minutes, every few hours, can help to reduce swelling from student's elbow
- Medication: Over the counter medication such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatories e.g. ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling from elbow bursitis
- Elbow Pads: You can protect your elbows and take the pressure off the olecranon bursa by wearing elbow pads or cushioned wraps. These allow the bursa time to heal and reduce the risk of future episodes of olecranon bursitis
- Avoid: Any activities that put direct pressure through the elbow such as resting your arm on arm rests or table edges, or repetitive elbow movement such as throwing sports should be avoided as much as possible
- Antibiotics: If you have an infection associated with olecranon bursitis then your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Take them as recommended and make sure you complete the course, even if the swelling has already settled down
- Aspiration: Your doctor may suggest draining the fluid if your elbow swelling is extensive. They may also inject some corticosteroid at the same time to reduce pain and inflammation. It is common for the fluid to re-accumulate so it can help to wear tubigrip compression bandage for a few weeks to prevent this
- Surgery: If your olecranon bursitis fails to improve after 3-6 months, or you have repeated episodes of elbow bursitis, then your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the bursa completely, known as a bursectomy. Following surgery you will be given a splint to wear initially and exercises to ensure you have full range of motion at the elbow. It usually takes around 3-4 weeks to fully recover from an olecranon bursectomy.
When To See Your Doctor?
Most cases of olecranon bursitis will settle down on their own with simple home treatment in a few weeks without the need for medical attention, but if you notice any of the following symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible:
- Elbow appears hot or red
- Elbow swelling is significant
- Elbow movement is restricted
- You have a high fever (38 degrees C or above) or chills
- You develop a rash or bruising around your elbow
- You have tachycardia – elevated heart rate
- You become confused or delirious
These would imply that there may be something other than student's elbow causing your pain.
Olecranon Bursitis Summary
Elbow bursitis is caused by excess fluid in the olecranon bursa, which may be caused by a one-off injury, repetitive friction/pressure or an infection at the elbow.
Olecranon bursitis causes soft, localised swelling at the back of the elbow that may develop over a few hours or several days. Elbow bursitis is the most common cause of a lump on elbow.
Elbow movement is rarely affected by olecranon bursitis but there may be some pain when the elbow is fully bent.
Signs of septic elbow bursitis include progressive swelling, redness, heat and posterior elbow pain and may cause you to feel unwell, such as having a fever. Septic olecranon bursitis requires immediate medical attention and will usually require antibiotics.
Non-septic olecranon bursitis can be treated with a combination of rest, avoiding aggravating activities, ice, compression bandages, elbow pads and medication. In some cases, your doctor may also recommend aspiration and/or corticosteroid injections.
In cases of elbow bursitis, symptoms will settle within a few weeks but in some cases, surgery may be required. It usually takes around 3-4 weeks to full recovery from olecranon bursectomy surgery.
Olecranon bursitis is also known as elbow bursitis, popeye elbow, student’s elbow, baker’s elbow, miner’s elbow, draftsman’s elbow, plumber’s elbow and swellbow.
If olecranon bursitis isn't sounding quite like your problem, visit the elbow pain diagnosis section for help working out what's wrong or check out the following articles:
- Pain Behind The Elbow
- Outer Elbow Pain
- Inner Elbow Pain
- Forearm Tendonitis
- Upper Arm Pain
- Arm Stretches
- Elbow Lumps & Bumps
Related Articles
Medical & Scientific References
- Olecranon Bursitis. NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS)
- Information About Olecranon Bursitis. NHS GG&C
Page Last Updated: March 27th, 2025
Next Review Due: March 28th, 2027