- Home
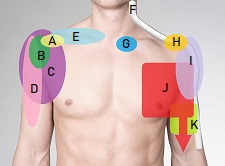
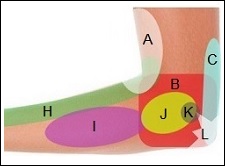
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis
- Pain Behind Elbow
Pain Behind The Elbow
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board
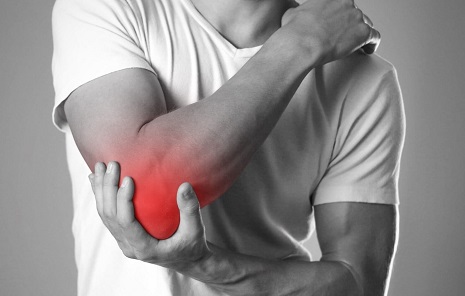
Pain behind the elbow is a common problem that affects people of all ages, from athletes to office workers.
There are lots of possible causes of back of elbow pain which may limit your daily activities and hobbies but in most cases it’s nothing serious.
There may be a general ache or a sharp pain behind the elbow, movement may be restricted and there may be some associated swelling.
What Causes Posterior Elbow Pain?
There are lots of possible causes of pain behind the elbow, often linked with inflammation and damage to the soft tissues. Here we will look at the most common causes of back of elbow pain and swelling, how to tell which one you have and then go on to look at how to treat them.
1. Elbow Bursitis
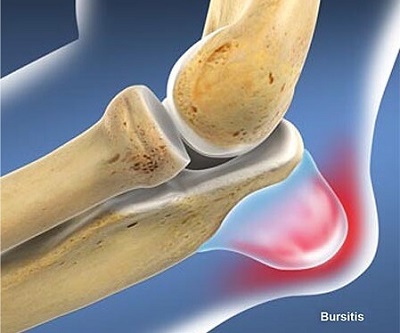
The most common cause of pain behind the elbow with swelling is Olecranon Bursitis, aka Students elbow.
The olecranon bursa is a small fluid filled sac found at the back of the elbow between the skin and the bone.
It helps to protect the elbow from injury and provides some padding so you can comfortably lean through your elbow.
Pain behind the elbow from bursitis may be caused by:
- Repetitive Pressure/Friction: through the bursa e.g. leaning through your elbow or repetitive ball throwing
- Elbow Injury: a sudden blow to the back of the elbow e.g. falling backwards
- Medical Conditions: that cause inflammation e.g. arthritis or an infection
With olecranon bursitis there is usually a defined pocket of swelling or elbow lump and pain at the back of the elbow, resembling a golf ball or small, squashy orange. The pain tends to be mild-moderate and gets worse when there is any pressure through the back of your elbow. Associated redness and warmth would indicate there is likely an infection.
There are lots of treatment options for swelling and pain behind the elbow from olecranon bursitis including ice, wearing elbow pads, activity modification, aspiration and medication. Occasionally, the bursa may need to be surgically removed.
You can find out all about the common causes, symptoms and treatment for swelling and pain behind the elbow in the Olecranon Bursitis section.
2. Triceps Tendonitis
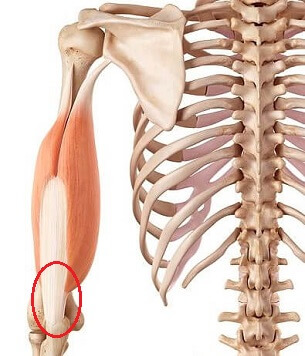
Another common cause of pain behind the elbow is triceps tendonitis, aka Weightlifter’s Elbow.
The triceps tendon is the thick cord-like structure that connects the triceps muscles that run down the back of the upper arm to the elbow. The main function of the triceps is to straighten the elbow but they also help with upper arm movement and shoulder stability.
Repetitive strain through the tendon leads to irritation, damage and tearing resulting in inflammation and pain behind the elbow.
Common causes of triceps tendonitis back of elbow pain include:
- Overuse: activities where you repeatedly straighten or overextend the elbow e.g. throwing sports, gymnastics, DIY, mountain biking and doing press-ups
- Injury: sudden overloading of the tendon e.g. lifting a very heavy weight
- Muscle Imbalance: weakness and or tightness in the upper arm muscles
Typical symptoms of triceps tendonitis include an aching pain behind the elbow that gets worse with activity, a snapping or popping noise when you straighten your arm, weakness and stiffness around the elbow and tenderness.
Treatment for triceps tendonitis focuses on reducing the inflammation and pain behind the elbow and restoring full motion, strength and flexibility. This usually involves a combination of rest, ice, medication, exercises, elbow braces, activity medication and physical therapy.
Pain behind the elbow from triceps tendonitis usually settles down within a few weeks if treatment is started promptly, but can take over a year if not.
You can find out how to reduce this cause of pain behind the elbow in the triceps tendonitis section.
3. Posterior Elbow Impingement
Another possible cause of back of elbow pain is posterior elbow impingement. Posterior elbow impingement pain develops when the elbow is repeatedly forced into extension and typically affects athletes partaking in over-head sports such as baseball, volleyball, tennis and swimming.
As the elbow is repeatedly thrust into extension, the olecranon process is forced into the groove at the back of the elbow, squashing the soft tissues that line the elbow joint, the synovium and cartilage. Over time, this results in inflammation and possible tearing of the joint lining resulting in pain behind the elbow and stiffness.
In some cases, the body tries to protect itself by laying down an extra layer of bone known as bone spurs, but these actually exacerbate the problem as they reduce the space in the joint making it more likely for the structures to get squashed.
Typical symptoms of posterior elbow impingement include tenderness and pain behind the elbow, which typically gets worse when straightening the arm, throwing over-head or with racket sports. The joint may become stiff and if one or more fragments of bone break off, they can actually block movement altogether.
There are a number of ways to treat posterior elbow impingement pain including corticosteroid injections, activity modification, strengthening and stretching exercises and physical therapy. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove any bone fragments.
4. Olecranon Fracture
Another possible cause of pain behind the elbow, especially after an injury, is an olecranon fracture. The olecranon is the bony tip of the elbow found on the end of the ulna bone. It is an important part of the elbow as a number of soft tissues attach to it, including the triceps tendon and various ligaments that move and stabilise the elbow. An olecranon fracture is where there is a break or crack in the back of the elbow bone.
Olecranon fractures can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Direct Impact: A direct blow to the elbow, such as from a fall or a sports injury
- Repetitive Stress: Overuse or repetitive stress on the elbow joint, e.g. from playing sports like tennis or baseball, can weaken the olecranon and make it more prone to fracture
- Age-Related Changes: As we age, our bones become more brittle and are more susceptible to fractures
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as osteoporosis, bone cancer, or bone infections, can weaken the bones and make them more likely to break
Common symptoms of olecranon fractures include swelling and pain behind the elbow, obvious deformity if the bones are displaced, stiffness and difficulty moving the elbow and in severe cases, numbness and tingling in the hand if there is associated nerve damage.
Treatment for olecranon fractures will depend on the severity of the injury, but may involve immobilizing the arm with a cast or splint, using ice to reduce swelling, and taking pain medications. In some cases, surgery may be needed to realign the bone or to place screws, plates, or pins to hold the bone in place while it heals.
Recovery from an olecranon fracture can take several weeks or months, and physical therapy is recommended to help regain strength and mobility in the affected arm. With proper treatment and care, most people with olecranon fractures are able to return to their normal activities over time.
5. Tennis Elbow
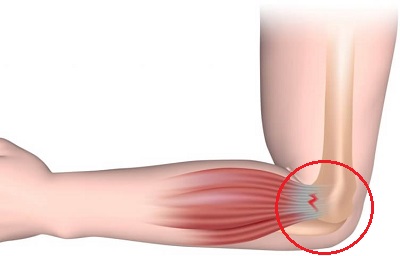
Pain behind the elbow that is towards the outer side of the joint is often caused by tennis elbow, aka lateral epicondylitis.
Lateral epicondylitis is an overuse injury that occurs when the common extensor tendon of the forearm muscles becomes inflamed and torn, leading to outer posterior elbow pain.
Tennis elbow can affect anyone, not just sports players, with office workers or manual workers being just as likely to experience it.
Symptoms of tennis elbow typically include posterolateral elbow pain (pain behind the elbow on the outer side), forearm weakness, decreased grip strength, and pain when performing twisting or gripping activities such as opening a jar or holding a cup.
Treatment for tennis elbow aims to first reduce pain and inflammation on the back and outside of the elbow, followed by improving strength and flexibility so that you can resume your normal activities without experiencing outside elbow pain.
If you want to learn more about how to reduce pain behind the elbow from lateral epicondylitis and the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, check out our Tennis Elbow section for comprehensive information.
6. Golfers Elbow
Another possible cause of pain behind the elbow that radiates around from the inner side of the joint is Golfer’s Elbow.
Golfer’s elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is a painful condition that arises due to the irritation and inflammation of the common flexor tendon that attaches to the medial epicondyle - a bony protrusion on the inner side of the humerus (upper arm bone).
Repetitive overuse of the forearm muscles that assist with gripping, twisting, and bending your hand and fingers is typically responsible for causing medial epicondylitis. Activities that can trigger inner elbow pain at the back of the elbow from golfer’s elbow include manual labour, racket sports, throwing sports, and heavy lifting.
The symptoms of golfer’s elbow commonly include tenderness and medial and posterior elbow pain that may extend down to the wrist. There is typically no pain in the hand, but the condition can cause weakness, making it difficult to perform gripping and twisting activities, such as opening jars.
The most common approach to treating golfer's elbow typically involves a combination of rest, modifying activities that aggravate the condition, engaging in targeted exercises to strengthen and stretch the forearm muscles, and potentially receiving injections. Some people also find it beneficial to use a specially designed elbow brace to support the affected area and reduce pain.
If you want to learn more about how medial epicondylitis causes medial and posterior elbow pain, including the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, our Golfer’s Elbow section has everything you need to know.
Other Causes Of Back Of Elbow Pain
There are a few other less common causes of pain behind the elbow including:
1. Elbow Arthritis
Gradual onset of pain behind the elbow in people over the age of 60 is often due to arthritis.
There are several types of arthritis that can affect the elbow joint, including osteoarthritis (wear and tear), rheumatoid arthritis (systemic inflammation), psoriatic arthritis and gout.
2. Tumor
Tumors that may cause pain behind the elbow include bone tumors (such as osteoid osteoma), soft tissue tumors (such as lipoma or synovial sarcoma), or metastatic tumors that have spread to the bones or soft tissues around the elbow.
However, it's important to note that tumors are a relatively rare cause of posterior elbow pain and are usually accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, deformity, or a visible lump.
3. Elbow Apophysitis
Pain behind the elbow in children may be caused by elbow apophysitis. Elbow apophysitis, also known as Little League elbow or throwing elbow, is a condition that affects young athletes who participate in throwing sports. It occurs when repetitive stress is placed on the growth plate of the elbow joint, causing inflammation and pain. The pain is usually felt on the inside of the elbow and can radiate to the back of the elbow.
Treatment For Posterior Elbow Pain

Treatment for pain behind the elbow will depend on the underlying cause and how severe your symptoms are.
It will usually involve a combination of resting the affected area, modifying activities that cause pain, and performing strengthening and stretching exercises to help relieve symptoms.
Other treatments may include ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain medications, and physical therapy. In some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
Mild cases of pain behind the elbow may resolve with rest and conservative treatment measures within a few weeks. However, more severe cases such as fractures or tendinitis may take several months to fully recover. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the best course of treatment and recovery time for your back of elbow pain.
Pain Behind The Elbow Summary
Pain behind the elbow is a common problem that can affect people at any age.
A pocket of swelling behind the elbow is usually due to olecranon bursitis. More generalised swelling may be a sign of arthritis.
Pain behind the elbow that gets worse when using the arm is often from tendonitis or impingement, but may also be due to tennis elbow (outer elbow pain) or golfer’s elbow (inner elbow pain).
If there is an obvious deformity with your back of elbow pain then you may have an olecranon fracture.
Treatment for pain behind the elbow will depend on the underlying cause but may involve a combination of medication, rest, ice, exercises, physical therapy and injections. The earlier you start treatment, the quicker the posterior elbow pain is likely to improve.
You may also be interested in the following articles
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis Charts
- Elbow Range Of Motion
- Inner Elbow Pain
- Outer Elbow Pain
- Elbow Lumps
- Arm Nerve Pain
- Upper Arm Pain
- Arm Stretches
Page Last Updated: 27th March, 2024
Next Review Due: 27th March, 2026
Related Articles
Shoulder Problems
November 6th, 2024
Diagnosis Charts
June 25th, 2025
Elbow Diagnosis
February 28, 2025