- Home
- Wrist Pain Diagnosis
- Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion Cyst Wrist
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board

A ganglion cyst on the wrist is a common, benign lump that develops on the wrist or hand.
These fluid-filled sacs are usually painless but can cause discomfort, especially if they press on nearby nerves.
While wrist ganglions are not dangerous, they can be bothersome, affecting wrist movement and function.
Here we will look at what a ganglion cyst is, the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and when to consider surgery.
What Is A Ganglion Cyst Wrist?
A ganglion cyst wrist is a non-cancerous, fluid-filled lump that can develop anywhere in the wrist or hand. It is the most common cause of a wrist lump.
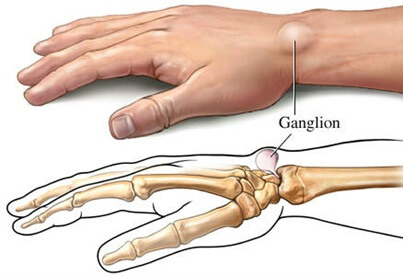
Ganglion cysts grow out of the synovial membrane around a joint or tendon sheath.
Thick, gel-like fluid leaks out and collects in a sac-like structure, forming a lump on the wrist.
Think of it like a tiny water-balloon on a stalk, connected to the joint or tendon.
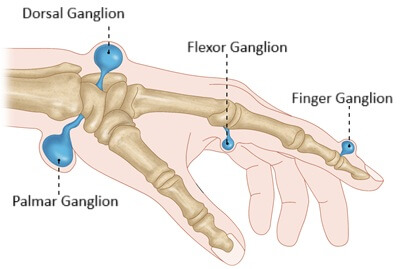
Ganglion wrist cysts can vary in size, from pea-sized to the size of a golf ball. They can develop anywhere around the wrist or hand, but are most common on the back of the wrist (60-70%).
A ganglion cyst wrist is usually completely harmless, and in most cases, doesn’t cause any pain, but if they start to press on nearby structures e.g. nerves, they can cause discomfort, altered sensation or limit movement. This is most common in cysts located in the palm rather than those on the back of the wrist.
What Causes A Ganglion Cyst Wrist?
Ganglion cyst wrist causes are often unknown, but several factors may contribute to their development:
- Joint or Tendon Irritation: Repetitive movements or excessive wrist strain may lead to cyst formation e.g. gymnasts
- Trauma: A previous wrist injury or repetitive stress on the joint may trigger cyst development due to excess fluid around the injury site. Accounts for around 10% of cases
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or degenerative joint conditions e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the likelihood of developing ganglion cysts
- Age & Gender: Wrist ganglion cysts are more common in women and typically occur in individuals between 20 and 40 years old.
Ganglion Cyst Wrist Symptoms
A ganglion cyst wrist may present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Visible Lump: A round or oval bump, usually soft or firm is the most obvious wrist ganglion symptom. The average size of a wrist ganglion is 1-2cm. They can be so small that they go unnoticed, known as occult ganglions
- Pain or Discomfort: Most wrist ganglions are completely painless, but some cysts press on surrounding structures, causing dull pain, aching, or tingling sensations in the forearm, wrist or hand. Ganglion cyst wrist pain is usually fairly mild and people generally describe it as annoying rather than debilitating
- Tenderness: there may be some discomfort if you press on the wrist ganglion
- Size Fluctuations: The cyst may grow larger with wrist use and shrink after periods of rest. They may develop rapidly or slowly
- Limited Mobility: Larger cysts may restrict wrist movement
Diagnosis and When to See a Doctor
A doctor can typically diagnose a ganglion cyst on wrist through a physical examination. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Visual Inspection & Palpation: The doctor will assess the ganglion cyst’s size, shape, and mobility
- Transillumination Test: They may shine a light through the lump - if the light passes it, causing it to “light-up”, it is likely a fluid-filled cyst rather than a solid mass
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may be used to rule out other conditions like arthritis or tumors
You should seek medical advice if:
- The cyst is causing significant pain or limiting wrist function
- The lump grows rapidly or changes in appearance
- You experience numbness, weakness, or tingling in the wrist or fingers
Whilst ganglions cysts are the most common cause of a lump on the wrist, there are a number of other things that can cause wrist lumps, such as a wrist fracture, giant cell tumor, carpal boss or epidermoid cyst – find out more in the lump on wrist section.
#CommissionsEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Wrist Ganglion Treatment
Most wrist ganglions are harmless and do not require treatment, unless they start causing pain, affecting function or are particularly unsightly. If this happens, ganglion cyst wrist treatment options include:
- Observation: Many cysts disappear on their own without intervention so if there is no pain or interference with daily activities a wait and watch approach is the best course of action
- Immobilization: Wearing an wrist support for ganglion cyst reduces wrist movement which can help the cyst to reduce in size and in turn reduce ganglion cyst wrist pain
- Aspiration: A doctor may drain the fluid in a ganglion cyst on the wrist with a needle, but cysts often recur after this procedure. This is most commonly done for lumps on the back of the wrist, palmar ganglions are harder to aspirate as they tend to be near major blood vessels and nerves
- Corticosteroid Injection: Can help to reduce swelling and discomfort, but does not prevent recurrence
Ganglion Cyst Wrist Surgery
If the cyst is persistent, painful, or interfering with daily activities, wrist surgery for ganglion cyst may be recommended:
- Ganglion Cyst Excision: This procedure removes the cyst and its root, reducing the likelihood of recurrence
- Minimally Invasive vs. Open Surgery: Surgery can be done arthroscopically (with small incisions) or through traditional open surgery. Arthroscopic wrist ganglion surgery leads to less pain and scarring but open surgery has a slightly lower recurrence rate
- Recovery: Post-surgery, mild swelling and discomfort may last a few weeks, with full wrist function typically returning within a few months. You will be given a sling to wear to keep the hand elevated to reduce swelling, and will need to wear a wrist splint for a few days. The surgeon may recommend a course of physical therapy to work on strengthening and motion exercises until you regain full function.
Ganglion Cyst Wrist Summary
Ganglion cysts on the wrist are common, harmless lumps caused by collections of fluid leaking from joints or tendons.
They can affect people of any age and often fluctuate in size, averaging 1-2cm in diameter. Ganglion cysts are the most common cause of a lump on the wrist.
While a ganglion cyst on wrist is often painless, they can cause discomfort and affect wrist and hand function. Diagnosis is typically straightforward, and many cysts resolve without treatment.
If symptoms persist, aspiration or immobilization in a wrist brace may help, while surgery offers a longer-term solution in severe cases. If you experience pain, limited mobility, or rapid changes in cyst size, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Wrist Lumps
- Wrist Tendonitis
- Wrist Fractures
- Inner Wrist Pain
- Outer Wrist Pain
- Central Wrist Pain
- Ganglion Cyst Foot
- Bones Of The Hand
Related Articles
Page Last Updated: December 10th, 2025
Next Review Due: December 10th, 2027